CREDIT: NOAA's Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory
On Posted on by AOML Communications to Ocean Chemistry and Ecosystems
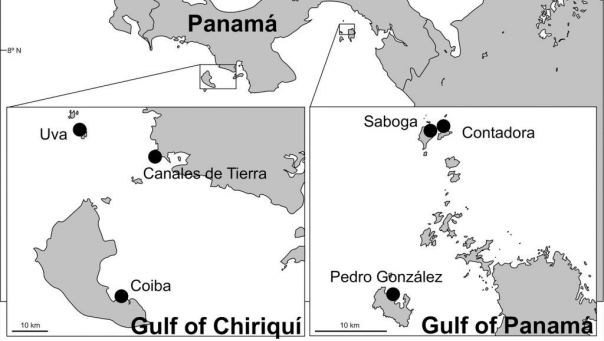
Location of the three study sites in each of two gulfs on the Pacific coast of Panamá.
Trying to predict how coral reefs will respond to warming oceans and a changing climate may be considered a daunting task for scientists. In the face of this challenge, scientists at AOML recently published a study that characterizes the organisms and processes that lead to coral reef accretion (build up) and bioerosion (break down) in the dynamic environments of the Gulf of Panamá and Gulf of Chiriquí in the eastern Pacific.
So how does a reef take shape and create pillars, ridges, and mountainous structures? Ocean conditions such as temperature, acidity, and available nutrients in the water play a role, as do marine organisms called “bioeroders” that graze the coral for algae (grazers), create holes in the coral surface (microborers), or create holes in its internal structure (macroborers). Although grazing and erosion diminish reefs, they also allow space for new coral to form through the deposition of calcium carbonate–a process called “calcification.”
Marine conditions such as temperature, acidity and available nutrients in water, have a certain influence and role, including those who are called "biological erosion" sea creatures for algae into coral survival domain, and making holes in the coral surface (microporous worm), or in the internal structure of coral hole (a big hole bug). While such erosion reduces coral reefs, the laws of nature, both positive and negative, pull them together to provide room for new coral formation, through the deposition of calcium carbonate, a process known as calcification.
Ian Enochs, a research ecologist from AOML and lead author of the study, said: "Coral reefs are facing a quantitative battle as the impacts of climate change intensify, not only reducing habitat growth but also increasing the risk of erosion. The stakes are high, and the resilience of coral reefs and the ecosystems they support are worth considering.
Scientists studied the marine organisms and processes mentioned above using bioerosion accretion replicates (BARs) made from stony coral (Porites) skeletons (the same material that makes up the reef), that were deployed to reefs in the gulfs of Panamá and Chiriquí. After two years, they scanned the BARs using computed tomography (CT) to better understand bioerosion and accretion at these reef sites.
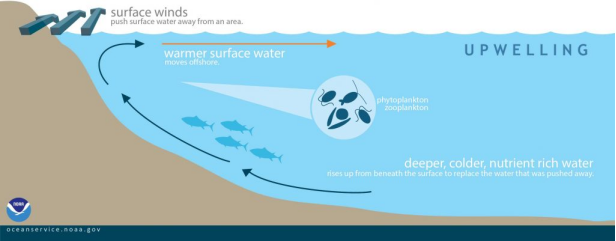
Surface waters are displaced by cold, nutrient-rich water that “wells up” from below in a process called “upwelling.” The water that rises is often cooler and more acidic, and may contribute to increased biological productivity from the nutrients it brings to the surface. Image from https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/upwelling.html
The study revealed that in both gulfs, external bioerosion by grazers such as parrotfish and urchins was the major process altering coral reef habitat, with higher rates of erosion and habitat loss observed in the Gulf of Chiriquí. One difference in environmental factors between the gulfs was the greater amount of upwelling (movement of deeper cold nutrient-rich waters to the surface) in the Gulf of Chiriquí that may have provided a food source for calcifying animals, as well as accelerated macroboring, leading to a less structurally stable reef developed on sediment (instead of solid reef material).
Keeping up with sea level rise and other stressors brought on by climate change presents a challenge for reefs struggling to grow and adapt to changes in the environment. The interaction of reef structure, habitat biodiversity, and ocean conditions can lead to a variety of ecosystem outcomes that are difficult to predict. A holistic approach to examining the impact of environmental conditions on all habitat-altering organisms is key to understanding reef persistence in the eastern Pacific and global ocean.
(CREDIT: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration)